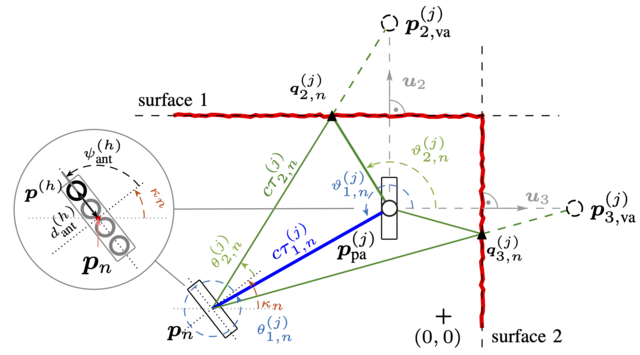
Accurate indoor localization using radio signals exchanged between base stations (BSs) and mobile dives (such as mobile phones) remains a challenging issue. This capability is essential for various critical applications, including search-and-rescue operations and autonomous navigation. We have recently developed a Bayesian particle-based sum–product algorithm (SPA) for multipath-based simultaneous localization and mapping [1, 2] that accounts for non-ideal reflective surfaces by jointly estimating dispersion parameters for individual physical and virtual anchors. This thesis provides the opportunity to work on state-of-the-art Bayesian inference methods for next-generation wireless localization systems.
Contact