How do we actually define intelligence? This question still has no clear answer. Without an answer, however, it is difficult for us to understand what artificial intelligence actually is. Generally speaking, "artificial intelligence" today is understood to be algorithms that learn independently in different ways based on given data and can then make decisions. For example, whether a dog is visible in a picture. But they also help researchers to recognise patterns and structures in vast amounts of data - also known as Big Data - they improve medical imaging or support vehicles on their way to autonomy.
At TU Graz, researchers are working on and with artificial intelligence in very different fields.
“For AI, an image is just a field of numbers”
Thomas Pock conducts research into image processing using artificial intelligence at the Institute of Computer Graphics and Vision at TU Graz. A conversation about the sunny and shadowy sides of technology.
Kern: “The Potential of AI Makes Me Optimistic”
Roman Kern conducts research in artificial intelligence at the Institute of Interactive Systems and Data Science at TU Graz. A conversation about the future of AI and general concerns about the topic.

Significant Energy Savings Using Neuromorphic Hardware
Research published in Nature Machine Intelligence illustrates neuromorphic technology is up to sixteen times more energy-efficient for large deep learning networks than other AI systems.

TU Graz research: Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence and machine learning as the most important tools of the future are the focus of the TU Graz research magazine.

Podcast: Robert Legenstein on Artificial Intelligence
Robert Legenstein is a computer scientist at TU Graz and heads the Institute of Theoretical Computer Science. He researches artificial neural networks and tells us about his work.
Simulated Brain Model Made to See for the First Time
Researchers at TU Graz have for the first time reproduced the function of vision on a detailed model of the mouse brain.
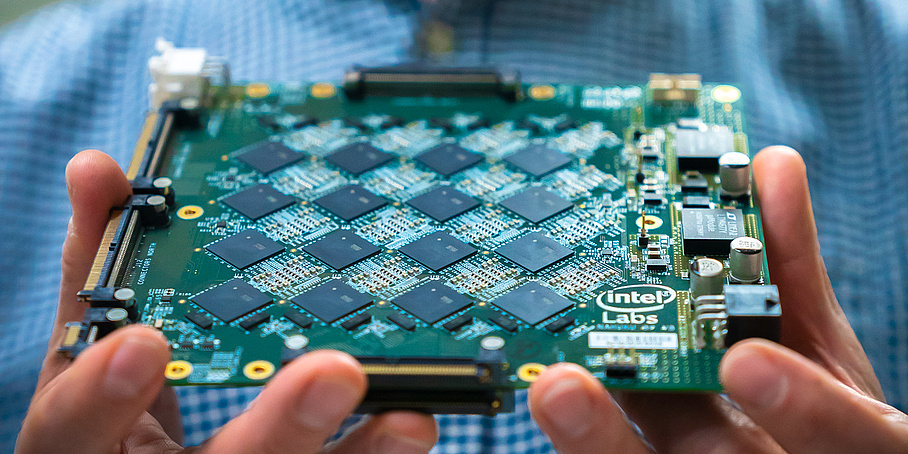
Significant Energy Savings Using Neuromorphic Hardware
Research published in Nature Machine Intelligence illustrates neuromorphic technologiy is up to sixteen times more energy-efficient for large deep learning networks than then other AI systems.

New AI Sensor Technology for Autonomous Driving
Researchers at TU Graz have modelled an AI system for automotive radar sensors that filters out interfering signals caused by other radar sensors and dramatically improves object detection.
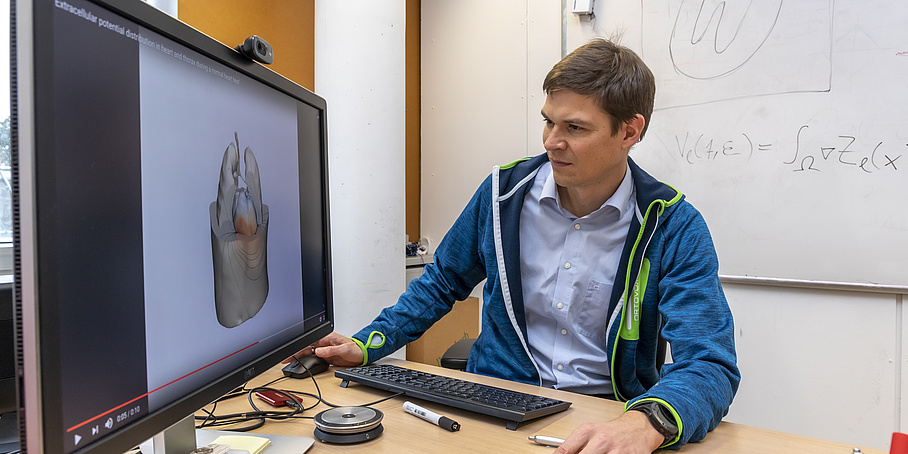
Play video
Video: What is Machine Learning?
Thomas Pock, researcher at the Institute of Computer Graphics and Vision at TU Graz explains what machine learning is and what it has to do with artificial intelligence.