- Duration of study: 6 semesters
- ECTS credit points: 180
- Academic degree: Bachelor of Science (BSc)
- Language of instruction: German,
some courses in English.
The Bachelor's Programme
In the Bachelor's Degree Programme Biomedical Engineering, you will receive a comprehensive basic education in the fields of technology, medicine and the natural sciences. The combination of these subjects makes this degree programme unique: You will gain knowledge in engineering and the natural sciences, a basic biological-medical education as well as the fundamentals of computer science. Your curriculum also includes an introduction to safety aspects and required regulations in medical technology. In addition, you have a chance to explore biomedical engineering in more detail and learn more about the areas of specialisation in the Master's Degree Programme Biomedical Engineering.
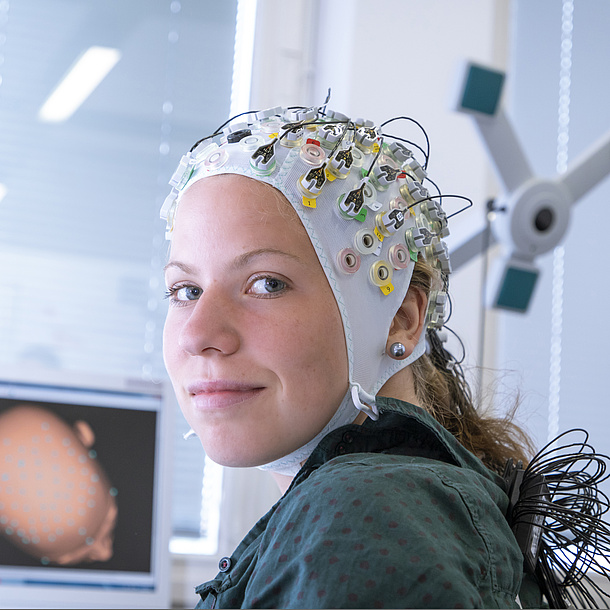
Students in this programme have access to excellent research infrastructure. This includes a state-of-the-art instrument for 3T magnetic resonance tomography (3T-MRT) or devices used to conduct brain research, such as EEG, near-infrared spectroscopy or fMRI instruments. Students can also use a modern biomechanics laboratory to carry out micro- and macroscopic tissue examinations, as well as a cellular electrophysiology laboratory.
During your degree programme, you will already gain helpful practical insights into business aspects of biomedical engineering. In numerous lectures, you will learn how tasks are dealt with in practice, e.g. in the field of medical device safety or using diagnostic imaging procedures. In addition, various parts of the curriculum have been designed to introduce you to institutes in which biomedical engineering is carried out, also in the "real" business world. While conducting bachelor’s thesis work, you will have the opportunity to work experimentally, program software, or learn about how specific hardware is built.
Studying Biomedical Engineering
You gain specialised knowledge in the following subject areas:
Medicine and Natural Sciences: You will learn the basics of physics as well as general and organic chemistry. In addition, you will learn more about human anatomy and physiology and find out how to consider these when developing technical systems. You will also receive an introduction to the subject areas of biochemistry, molecular and cell biology.
Mathematics: You will gain skills in applying basic mathematical concepts and methods and become familiar with, among other things, sequences and series, differential and integral calculus, functions, probability theory and statistics.
Electrical Engineering: You will gain knowledge about basic phenomena encountered in electrical engineering and learn how to describe them, as well as how to perform calculations for simple electrical circuits. You will learn how to analyse and dimension circuits and acquire basic knowledge about measurement technology. Furthermore, you will become familiar with systems and signal processing.
Mechanics: You will gain knowledge in the areas of statics, dynamics and biomechanics and learn how to apply this knowledge to solve biomedically relevant problems. Furthermore, you will become familiar with basic physical theories and topics relevant to biology, such as diffusion or electrodynamics.
Computer Science: You will learn more about the structure and function of computer systems and gain basic knowledge about programming and data science. In addition, you will receive an introduction to scientific computing using the MATLAB/Simulink software environment and become familiar with the terms and methods used in the field of machine learning.
Biomedical Engineering: You will learn more about general and specific aspects of the field, such as diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, biomedical measurements, as well as the basic principles of bioinformatics. This module also places a focus on conveying the basics of medical imaging.
Soft Skills and Bachelor Paper: You will gain insight into bioethical issues and learn how to reflect on and consider different ethical concepts. To help you prepare your bachelor paper, you learn how to conduct literature research, critically analyse a topic and produce a scientifically structured publication.
Elective Module Biomedical Engineering: You can choose from among various advanced and in-depth courses from the interdisciplinary department of Biomedical Engineering.
What will I have to do in the first semesters? How much practice can I expect? And what can I actually do with my degree when I've finished? Check what you expect!
Colleagues from the faculty will take time for you and your questions online:
To the Discord server of the Faculty of Computer Science and Biomedical Engineering
Contact: lse@tugraz.at

I study biomedical engineering because I learn technical things like programming and, at the same time, immerse myself in the world of medicine.
Many people don’t know what I do the first time I tell them what I study. But as soon as the terms
hospital technologyandmedical devicesare used, everything becomes clear. What I like most about Biomedical Engineering is the emphasis on the technical side with programming and electrical engineering. At the same time, I can also learn anatomy, biology and chemistry in detail.
We are living in a society with an increasingly older population. This requires new solutions to be found for safe, cost-effective, and efficient healthcare as well as new innovative medical devices.
Many advances can be made in the biomedical engineering field by developing new technical methods and scientific processes. For example, new materials enable the use of transient implants (i.e. implants that dissolve in the body) or minimally invasive operations can be performed using image-guided techniques.
The development of methods and devices for non-invasive biosignal measurement makes it possible, for example, for diabetes patients to measure and digitally evaluate their blood sugar levels using a biosensor. The use of rapid medical imaging methods also makes an important contribution to society.
A research project currently being carried out at TU Graz in the field of biomechanics, for example, will also provide important results. Researchers are working intensively on the mechanics, modelling, and simulation of aortic dissections. The aim of this project is to better understand chronic and acute aortic dissections (i.e. tears in the aortic wall) and to support physicians in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of patients with aortic dissections.
Admission
Requirements for admission to a bachelor's degree programme at TU Graz
Summer semester 2026
Admission period: 7 January to 5 February 2026
Winter semester 2026/27
Admission period: 6 July to 5 September 2026
Contact study@tugraz.at
Perspectives for Graduates
Graduates of the Bachelor’s Degree Programme are qualified to apply for the Master’s Degree Programme Biomedical Engineering or can begin a career in this field after receiving their academic degree.
Biomedical engineers have diverse career options in the areas of industry and research and development, for example:
- as manufacturers of medical devices,
- in medical device servicing, maintenance, and testing,
- as technical safety officers or technical safety representatives (TSB) and medical product consultants,
- in the development of research methods and tools, and development and production in the biotech and pharmaceutical industries,
- as calculation engineers for the development and optimisation of various implants such as stents,
- as software developers for medical devices,
- in the development and production of medications,
- in the development of new diagnostic procedures and therapies, and
- with regulatory authorities.
Possible careers in hospitals and the healthcare sector include careers as:
- risk managers,
- quality managers, and
- safety engineers.
After completing the bachelor's degree programme, you can enrol in the following master’s degree programmes without further requirements:
- Advanced Materials Science
- Biomedical Engineering
- Electrical and Electronics Engineering
- Information and Computer Engineering
Information on other master's degree programmes with requirements you can find on the respective pages for the master’s degree programmes.
In addition, the bachelor's degree offers you the opportunity to apply internationally for master's degree programmes.