Trained Feedback Loop
We propose an entirely data-driven approach to estimating the 3D pose of a hand given a depth image. We show that we can correct the mistakes made by a Convolutional Neural Network trained to predict an estimate of the 3D pose by using a feedback loop. The components of this feedback loop are also Deep Networks, optimized using training data. They remove the need for fitting a 3D model to the input data, which requires both a carefully designed fitting function and algorithm. We show that our approach outperforms state-of-the-art methods, and is efficient as our implementation runs at over 400 fps on a single GPU.
Material
Presentation: ICCV'15 presentation, ICCV'15 poster Our results: Each line is the estimated hand pose of a frame. The pose is parametrized by the locations of the joints in (u, v, d) coordinates, ie image coordinates and depth. The coordinates of each joint are stored in sequential order.- NYU dataset of J. Tompson: ICCV'15 Init, ICCV'15 Feedback
Semi-Automatic 3D Annotation
While many recent hand pose estimation methods critically rely on a training set of labelled frames, the creation of such a dataset is a challenging task that has been overlooked so far. As a result, existing datasets are limited to a few sequences and individuals, with limited accuracy, and this prevents these methods from delivering their full potential. We propose a semi-automated method for efficiently and accurately labeling each frame of a hand depth video with the corresponding 3D locations of the joints: The user is asked to provide only an estimate of the 2D reprojections of the visible joints in some reference frames, which are automatically selected to minimize the labeling work by efficiently optimizing a sub-modular loss function. We then exploit spatial, temporal, and appearance constraints to retrieve the full 3D poses of the hand over the complete sequence. We show that this data can be used to train a recent state-of-the-art hand pose estimation method, leading to increased accuracy.
The subjects were asked to perform common hand articulations, as well as typical articulations for AR/VR interaction. For each subject we recorded 19 sequences, 18 of which contain the same hand articulation performed by each subject, and 1 sequence with individual articulation. We collected data from 4 subjects (1 male, 3 female) and approximately 63k RGBD frames (each around 15k). Data and annotations can be downloaded below. More annotations will be released soon :)
There is no proper documentation yet, but a basic readme file and a short manual on how to use the GUI are included. If you have questions please do not hesitate to contact us.
If you use the code, please cite us (see below).
Material
Presentation: CVPR'16 poster Datasets:- Synthetic dataset with ground truth 3D joint locations used for the evaluation of our method.
- Egocentric 3D hand pose dataset created with our method (used in our CVPR paper).
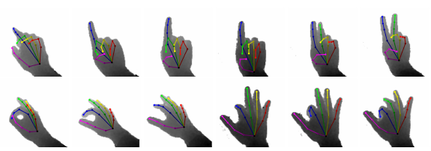
The subjects were asked to perform common hand articulations, as well as typical articulations for AR/VR interaction. For each subject we recorded 19 sequences, 18 of which contain the same hand articulation performed by each subject, and 1 sequence with individual articulation. We collected data from 4 subjects (1 male, 3 female) and approximately 63k RGBD frames (each around 15k). Data and annotations can be downloaded below. More annotations will be released soon :)
Code
Here you can find the code for our CVPR'16 paper "Efficiently Creating 3D Training Data for Fine Hand Pose Estimation". It is distributed as a single package SemiAutoAnno under GPLv3. The code can be run out-of-the-box with our synthetic dataset.There is no proper documentation yet, but a basic readme file and a short manual on how to use the GUI are included. If you have questions please do not hesitate to contact us.
If you use the code, please cite us (see below).
Contact
Record not found: Person
