Transient Stability Analysis and Post-Fault Restart Strategy for Current-Limited Grid-Forming Converter
Grid-forming converters are attracting attention for their significant advantages in terms of sta-bility in weak grid and simulated inertia. However, while they offer great flexibility due to the use of power semiconductors, they are also affected by their low current carrying capacity.
This means that during a fault instead of the ususalusual voltage control a current limiting control is active, which changes the dynamic performance of the converter and influences transient stabil-ity. This prevents a grid-forming converter from performing at its original dynamic perfor-mance under grid disturbances and leads to transient stability problems.
This manuscript focuses on the dynamic performance of grid-forming converters during the restart phase at the post-fault period, and proposes an initial phase threshold to prevent the converter from going into current saturation. Based on this, the manuscript proposes several restart strategies during the post-fault period, by using some fast resynchronization methods in order to meet the re-quirements of the converter’s stable operation and fast active power restoration.
Finally, the above findings and the proposed strategies are validated by a joint control hardware-in-the-loop system.
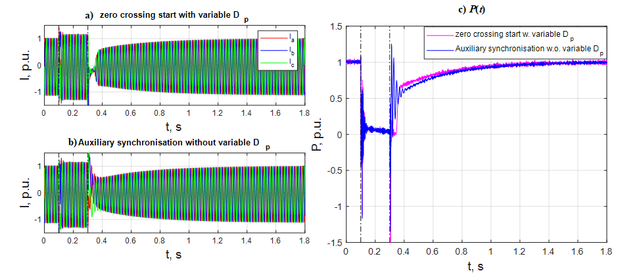
CHIL Test result: zero-crossing start with variable Dp, auxiliary synchronization without variable Dp. The utilization of auxiliary synchronization without variable droop factor Dp (blue curve) leads to similar power recovery times, and avoids start-up delays.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/en15103552
Paper donwload: https://mdpi-res.com/d_attachment/energies/energies-15-03552/article_deploy/energies-15-03552.pdf