Tomography Summer Camp 2025
During his internship, Felix has participated in our Tomography Summer Camp. From left to right, Selma Sejdic, Felix Reinprecht, Eduardo Machado, and Åsa Jerlhagen, a visitor from the KTH, Sweden.
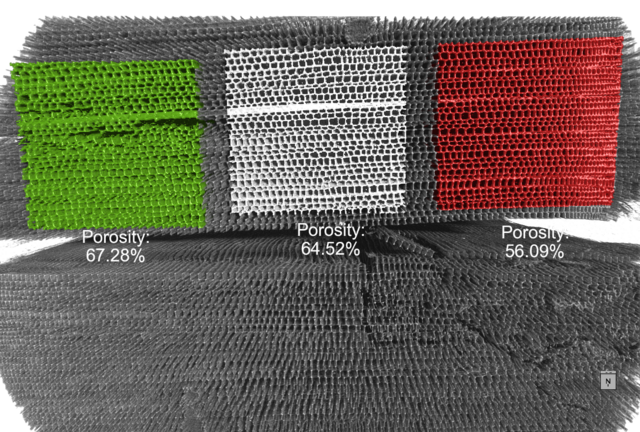
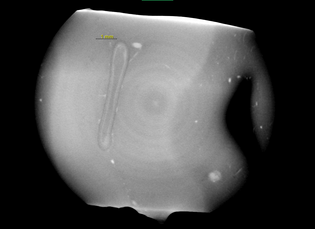
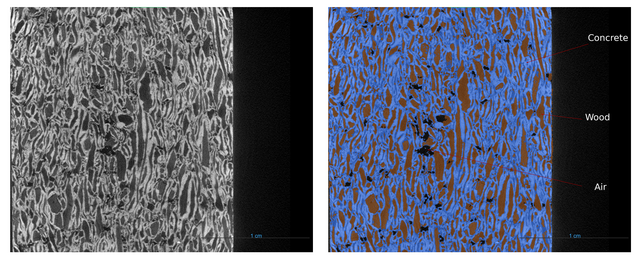
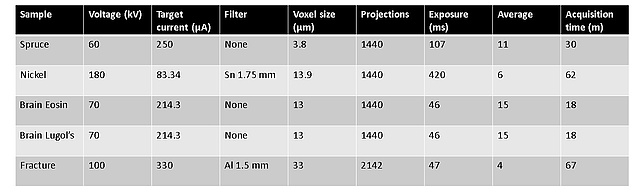
From the analysis of the microstructure of an anual ring inside the wood, he was able to see the evolution of the porosity of the tree along the year. At the left in the image the high porosity is related to spring, while on the right the low porosity is relate to winter. The acquisition parameters of this scan and the rest are listed on a table at the end of this page.
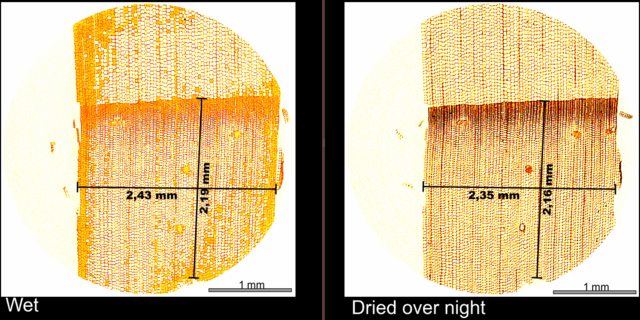
Felix left the sample in water overnight, scan it and then, let it dry overnight again. This simple experiment show us the swelling of the wood sample and the water uptake. The wood shows a swelling of around 3 % perpendicular to the anual ring growth direction and around 1.4% in the growth direction.
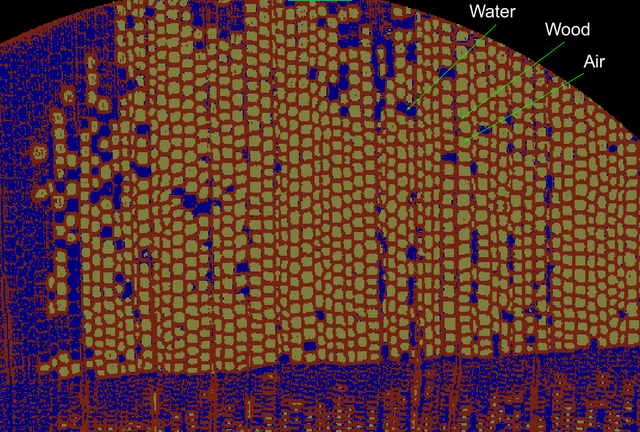
In this video, we can see the distribution of the water, now in orange, in the whole sample.
A video showing the porosity distribution in the sample. The segmentation was done with a U-Net deep learning model using the Segmentation Wizard tool implemented in Dragonfly 2024.1
This sample was prepared by Selma Sejdic with the help of Manuel Kainz and Clarissa Holzer-Stock from the Institute of Biomechanics at TUG. This simple sample setup was Selma's idea to hold the sample tight during the scan while avoiding drying.
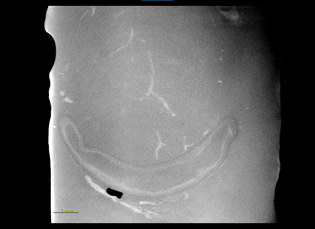
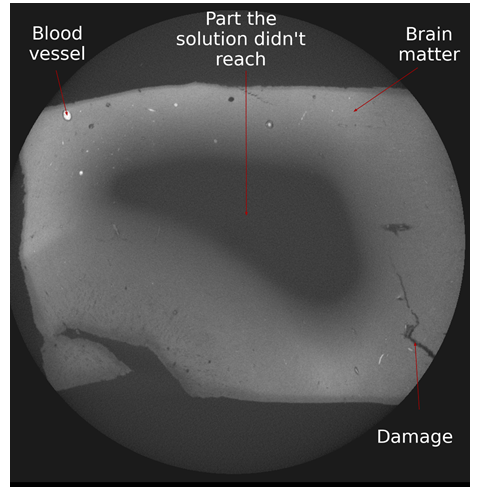
In this video, we can see some blood vessels in the brain. This segmentation was done with a Deep Learning Network. However, it is possible to see some false positives which look like a sphere.
As for the Eosin sample it is possible to see clearly some blood vessels, however, we were able to relate their position to the white matter in the brain.
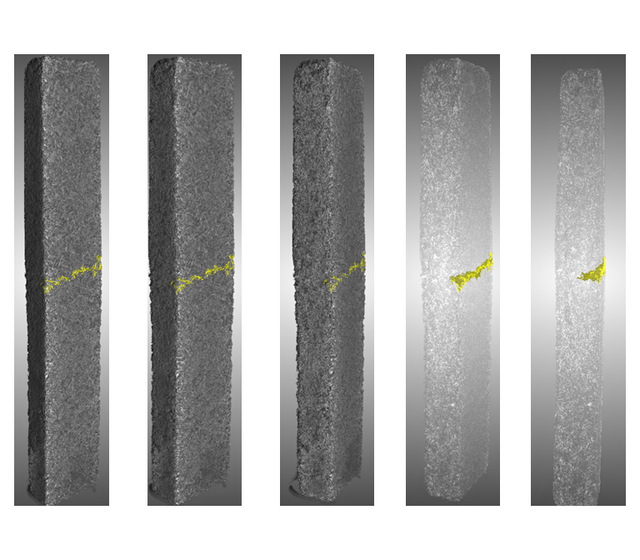
Fracture on concrete reinforced with wood.
A sample of concrete reinforced with wood from Univ.Prof. PhD Agathe Robisson at TU Wien was scanned along the whole height using the STAMINA mode. In this case, the goal was to determine the depht an induced fracture during a test.
The fracture was defined by the largest connected air cluster in the sample. But, it was necessary first to isolated the air related voxels inside the sample to those outside. Felix applied a Rolling ball algorithm to define the surface of the sample and morphological closing operation. These operations allow us to extract only the air clusters inside the sample. A close view of the fracture is in the video below.