Evolution natural (terrestrial) solutions
Specific tasks: Evolution of groundwater from volcanic areas (Ethiopia/Hessia/Azores)
Groundwater from volcanic aquifer is the main source of water supply for Axum town in semi-arid region of northern Ethiopia. Poor quality of groundwater from bore holes in the study area has been a major problem for the water supply.
The study aims to examine the effects of hydrochemical processes on the composition of groundwater using hydrochemical and isotopic tools. Stable isotopic (δ2H and δ18O) data suggest that the analyzed groundwaters are of meteoric origin. δ13CDIC values and solution composition indicate that the chemistry of shallow groundwater is controlled by the uptake of soil CO2 and silicates weathering. Abundant weathering of silicates in the deeper parts of aquifer is caused by the uptake of magmatic CO2 at high pCO2.
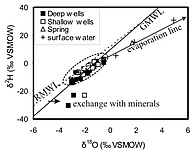
Figure (left): Relationships between δ2H and δ18O values for sampled solutions.
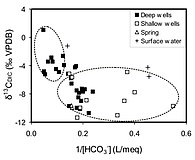
Figure (right): δ13CDIC values versus the reciprocal of HCO3− concentrations.
Contact: Martin Dietzel
Fossil groundwater (Libya / 17O excess)
Contact: Martin Dietzel
Evolution of groundwater from karst aquifers
Contact: Martin Dietzel