Kamonrat Suksumrit, Christoph A. Hauzenberger, Michael Gostencnik and Susanne Lux
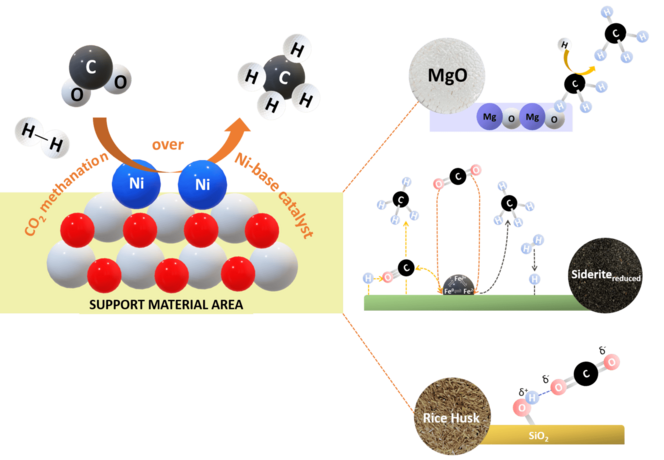
Catalytic CO2 methanation represents a promising process route for converting carbon dioxide into methane, a valuable energy carrier. This study investigates the performance of Ni-based catalysts on mixed silica and MgO support materials for CO2 methanation. Silica was derived from rice husk (SiO2(RH)), representing a sustainable, cost-effective source for catalyst support, and MgO was used as a reference and to enhance the catalytic activity of the Ni-based catalysts through admixture with SiO2(RH). The results were compared to CO2 methanation over Ni-based catalysts on reduced iron ore from natural siderite (sideritereduced), providing another abundant source for catalyst support. The experiments were conducted in a tubular reactor with a feed gas composition of H2:CO2:N2 = 56:14:30, feed gas flow rates ranging from 4.01 to 14.66 m3·kg−1·h−1 (STP), and reaction temperatures of 548–648 K. The highest CO2 conversion with the Ni/SiO2(RH) catalyst was 39.01% at a methane selectivity of 92.64%. The use of mixed silica and MgO supports (SiO2(RH)/MgO) for nickel revealed a beneficial effect, enhancing CO2 conversion and methane formation. In this case, methane selectivities consistently exceeded 91.57%. Superior methane selectivity and CO2 conversion were obtained with Ni/MgO catalysts and Ni/SiO2(RH)/MgO catalysts with high MgO fractions, highlighting the fundamental effect of MgO in the catalyst support for CO2 methanation.
MDPI Catalysts
DOI: 10.3390/catal15060589