Christoph Weinzettl, Paul Demmelmayer, Lukas Pachernegg-Mair, Michael Wernhart, René Rieberer, Roland Kalb, Marlene Kienberger
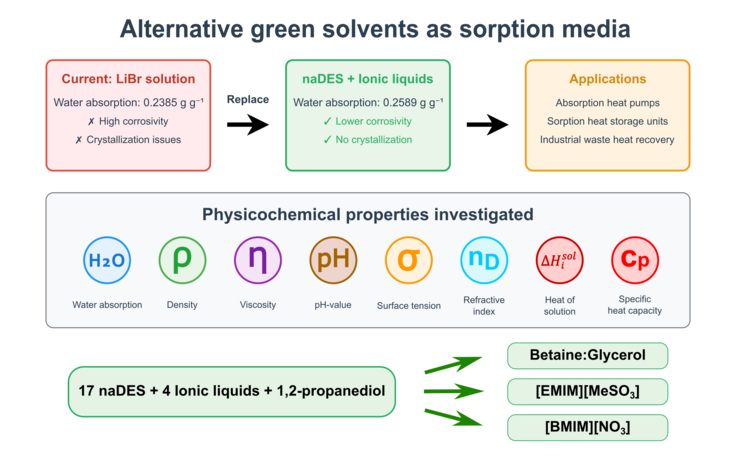
Hydrophilic natural deep eutectic solvents have been proposed for various applications, yet their physicochemical properties remain insufficiently characterized, limiting their potential as sustainable sorption media for absorption heat pumps and sorption heat storage units. This work provides a systematic evaluation of 17 natural deep eutectic solvents, four sustainably produced ionic liquids, and 1,2-propanediol. Density, viscosity, surface tension, and refractive index were measured across different temperature and water loads, and the heat of solution, specific heat capacity, and static water absorption capacities of selected solvents were determined. Several solvents achieved water absorption capacities up to 0.3239 g g−1, exceeding that of a 54 % (w/w) lithium bromide solution (0.2385 g g−1), the current state-of-the-art sorption media. Structural analysis revealed that water uptake negatively corelates with the numbers of carbon- and oxygen atoms, and positively correlates with nitrogen content. This finding is crucial for understanding how the constituents influence the behaviour of the solvents. Increasing temperature and water load led to exponential viscosity reductions, decreasing pumping energy requirements and simplifying hydrodynamic design. The generated property dataset provides essential engineering-relevant input for modeling, sizing, and evaluating alternative sorption media. The most promising candidates for sorption applications were betaine-glycerol as natural deep eutectic solvent and the ionic liquids [EMIM][MeSO3] and [BMIM][NO3], combining high water absorption capacity with manageable viscosity and stability. Overall, this study demonstrates the strong potential of sustainable solvents to replace lithium bromide and enhance the environmental performance of absorption heat pumps and sorption heat storage units.
Chemical Engineering Journal
doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2025.171586
Link to Article