IDE@S Use Cases for cross-organisational data exchange
Use case - µCT
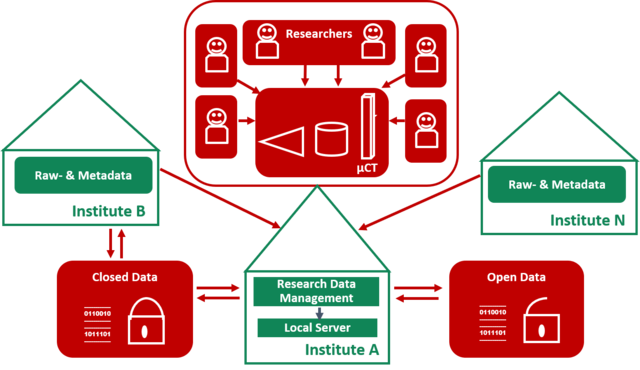
A consortium of 13 departments from three universities in Graz has been formed to steer the collective use of an X-ray micro-computer tomograph (µCT). This device will be used above all for basic scientific research, especially for Dynamic Computed Tomography (DCT). Research fields where this can be employed include kidney stones, fibril angle of paper fibre, polymorph structures in pills or the development of textures in metals, among others. In combination with an environmental chamber (i.e. a container that enables to control environmental conditions) the µCT will allow to study the effect of air humidity on the pore structure of paper, the setting process of concrete, or corrosion in alloy seams. An overarching goal of this interdisciplinary collaboration is to put efficient data analysis processes in place, which will require regular meetings with the users. The different expertise and know-how gathered by the research groups in "slicing" or sectioning of the materials employed will allow to gain new insight in this procedure and the related analysis of the images obtained.
To enable the management and exchange of raw- and metadata, as well as to simplify workflows and data archiving in all research fields, the consortium will start a data management platform accessible via website. The open source software used will require regular updates and long-term support from the development team for authentication, data exchange upon request, structured storage of digital objects using the Oxford Common File Layout (OCFL) specification, different file formats and update automation. Currently the security strategy and guidelines are under development. The main data storage facility will be provided by one of the participating departments to allow the data management software to be installed and enable the connection to other devices.
Use case - Smart energy systems

A dataplatform linked to a infrastructure for internet-of-things (IoT) at the TU Graz campus has been developed by researchers at the Department of software technology to be used for different energy-related services, e.g. von TU Gebäude und Technik oder EAM Systems. In one of the related projects, energy data are made available and analysed with the goal of actively involving users in the system. This will allow better planing and managing of energy systems that include a strong fluctuating usage and a big component of non-constant energy sources (in particular renewable energy). Using monitoring algorithms that employ real-time data from IoT devices, the platform can also be employed to implement "sustainable campus" solutions. Data exchange and data protection of sensitive user information as well as transparent control will be explored in a related project.
Use case - CyVerse
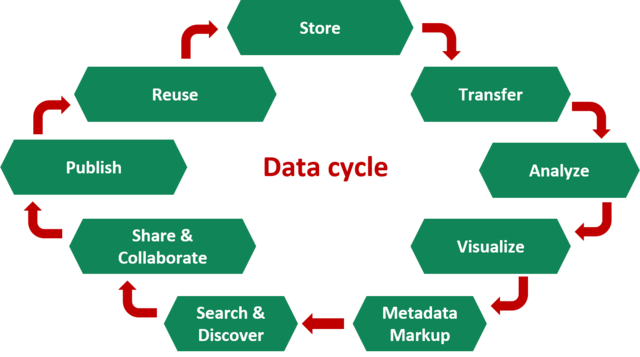
In the area of life sciences, a collaborative environment for management and analysis of large datasets that can be used by all universities in Graz has been started to reinforce data-driven science. The distributed computer architecture to organise the data, together with web-based data analysis, will help and provide support to researchers of all disciplines. Of all the possible implementations of Cyverse, the version used in Graz is distributed through the three participating universities of the BioTechMed consortium, with a current project exploring its expansion to other regions in Austria. The American version of this cyber-infrastructure has a longer history and already offers various services, including secure data storage, bio-informatics and interactive (web-based) analytics, visualisation, cloud connection to computational and storage facilities, and developer environment. Cyverse is managed by the University of Arizona together with the Texas Advanced Computing Center and Cold Spring Harbor Labor. As use case, already defined workflows to solve biomedical problems will be automated through the platform using container system to ensure their reproducibility for all the community. At the basis of the data management system lies standards and metadata procedures already established in the life science field. Of fundamental importance is the utilisation of FAIR Data principles for data, software solutions and other resources. The security strategy employed at its core uses GDPR directives already in place and incorporates further guidelines and standards of the partner organisations. In case of conflicting policies the stricter regulations are favoured.
Use case - Health data circles
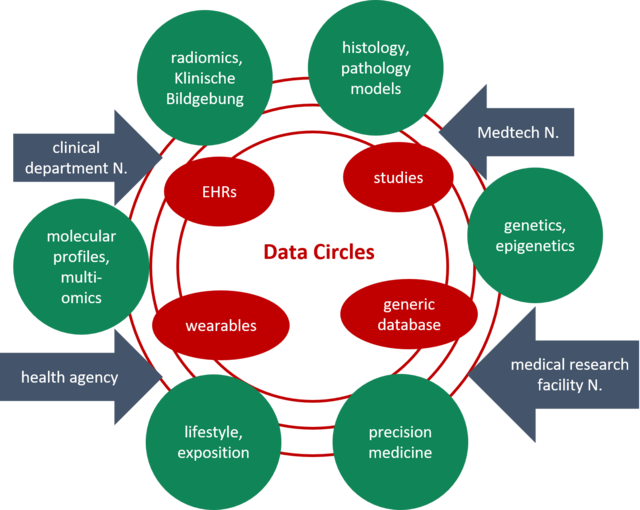
A consortium formed by research organisations and R&D businesses aims at enabl the use of training data for artificial intelligence (AI) generated at fragmented "data silos". Data silos are isolated storage devices controlled by a single organisation or authority. The data will be made available to develop models. Data circles brings data producers and users together, which will open new scenarios to apply the results. Data protection and quality and preservation of privacy are taken into account from the start to overcome lack of trust and other concerns that are typical of data marketplaces.
The project will also contact relevant stakeholders to create future data circles tailor-made to meet their requirements. By considering other ethical aspects like political issues as well, together with user interfaces, appropriate data processing, quality policies and legal framework, it is hoped it will be possible to demonstrate the added value of data circles for a secure data exchange. Data value assessment will also be developed and will also contribute to this end.
Current approaches to data security and sovereignity in a decentralised data collection environment will be expanded to include issues raised by the use of AI training data. To this end, quality standards at the meta-level will be integrated and made available in user guides. Data producers retain in this setup control over the allowed use of their data, ensuring data privacy is kept at all times. This will also make data flow traceability possible while conforming with national and international regulations. All partners contribute their legal expertise along with their previous experience in data quality, criptography, and explainable AI. The project also looks at avoiding discrimination in the use of AI by taking diversity perspectives into account, of particular importance when dealing with health-related data. The results of the project will be made available for the general public.
Dr Miguel Rey Mazón (m.reymazon@tugraz.at) Project manager
Institute for Interactive Systems and Data Science (ISDS)
Haus der Digitalisierung, Brockmanngasse 84, 8010 Graz
Graz University of Technology
