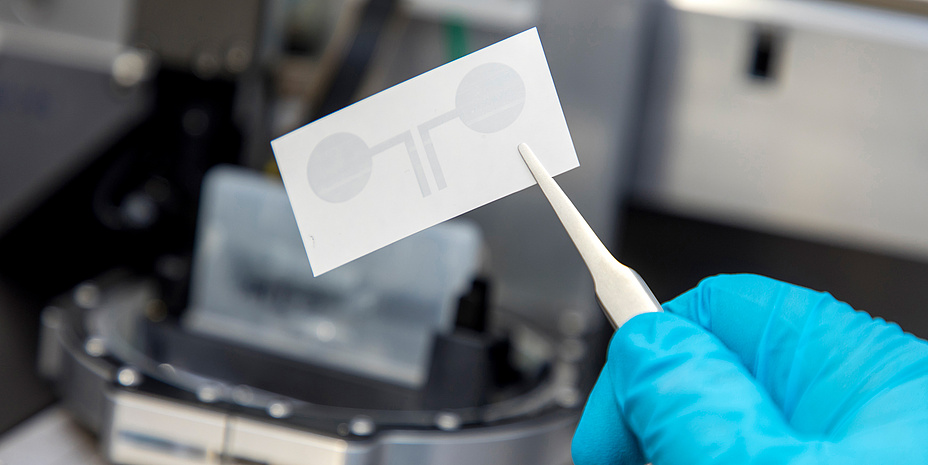
Tattoo electrodes from an ink-jet printer

In the case of diagnostic methods such as electrocardiogram (ECG) and electromyography (EMG), gel electrodes are the preferred method of transmitting electric impulses from the heart or muscle. In clinical practice the frequently stiff and cumbersome electrodes noticeably restrict the mobility of patients and are not very comfortable. Because the gel on the electrodes dries out after a short time, the possibilities of taking measurements over a longer period using this kind of electrode are limited. Together with researchers from Instituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT) Pontedera, Università degli Studi in Milan and Scuola Superiore Sant’ Anna in Pisa, Francesco Greco from the Institute of Solid State Physics at TU Graz presents a novel method in Advanced Science which raises the transmission of electrical impulses from human to machine to the next level using printed tattoo electrodes.
Printed tattoo electrodes for long-term diagnostics
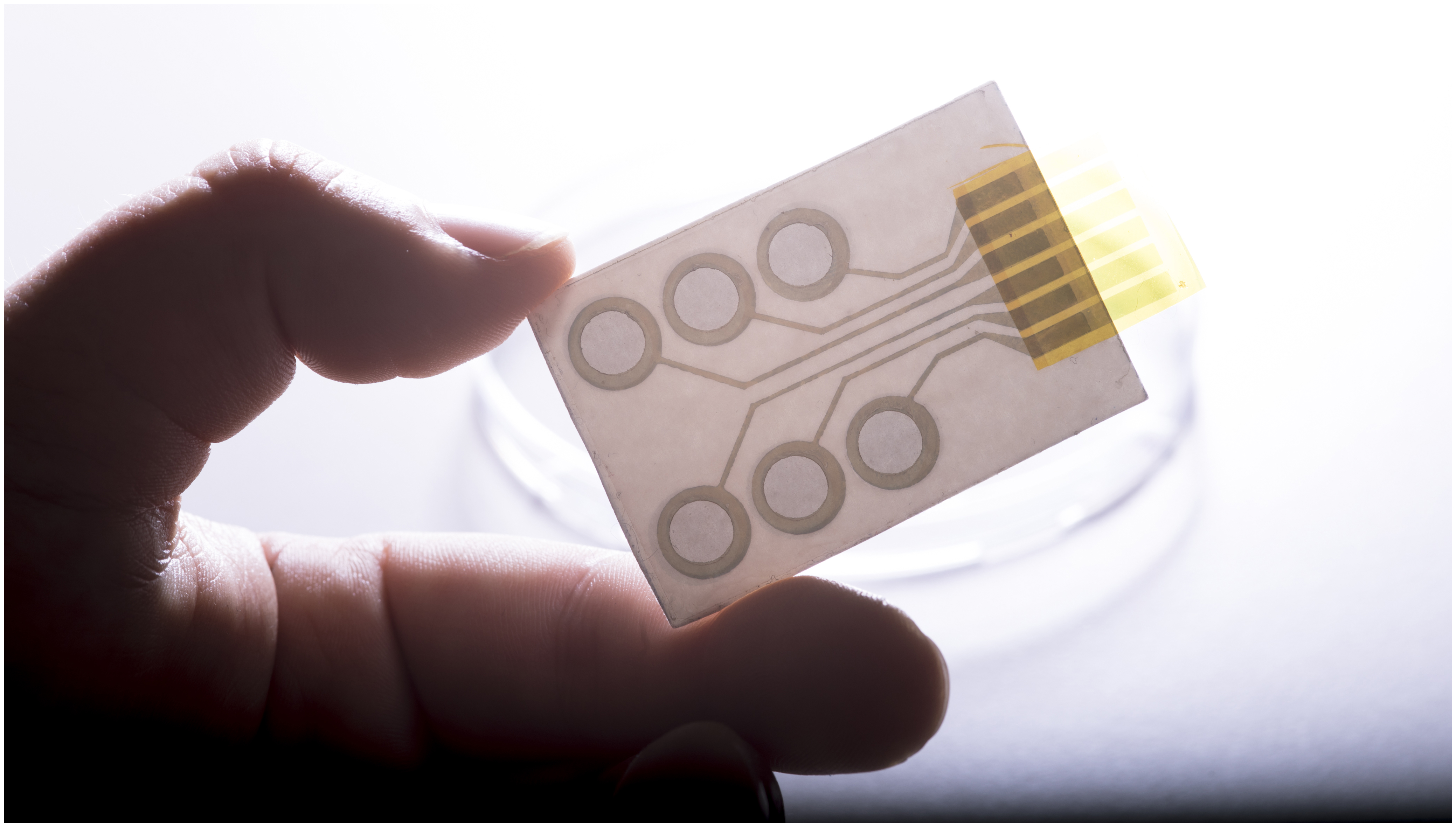
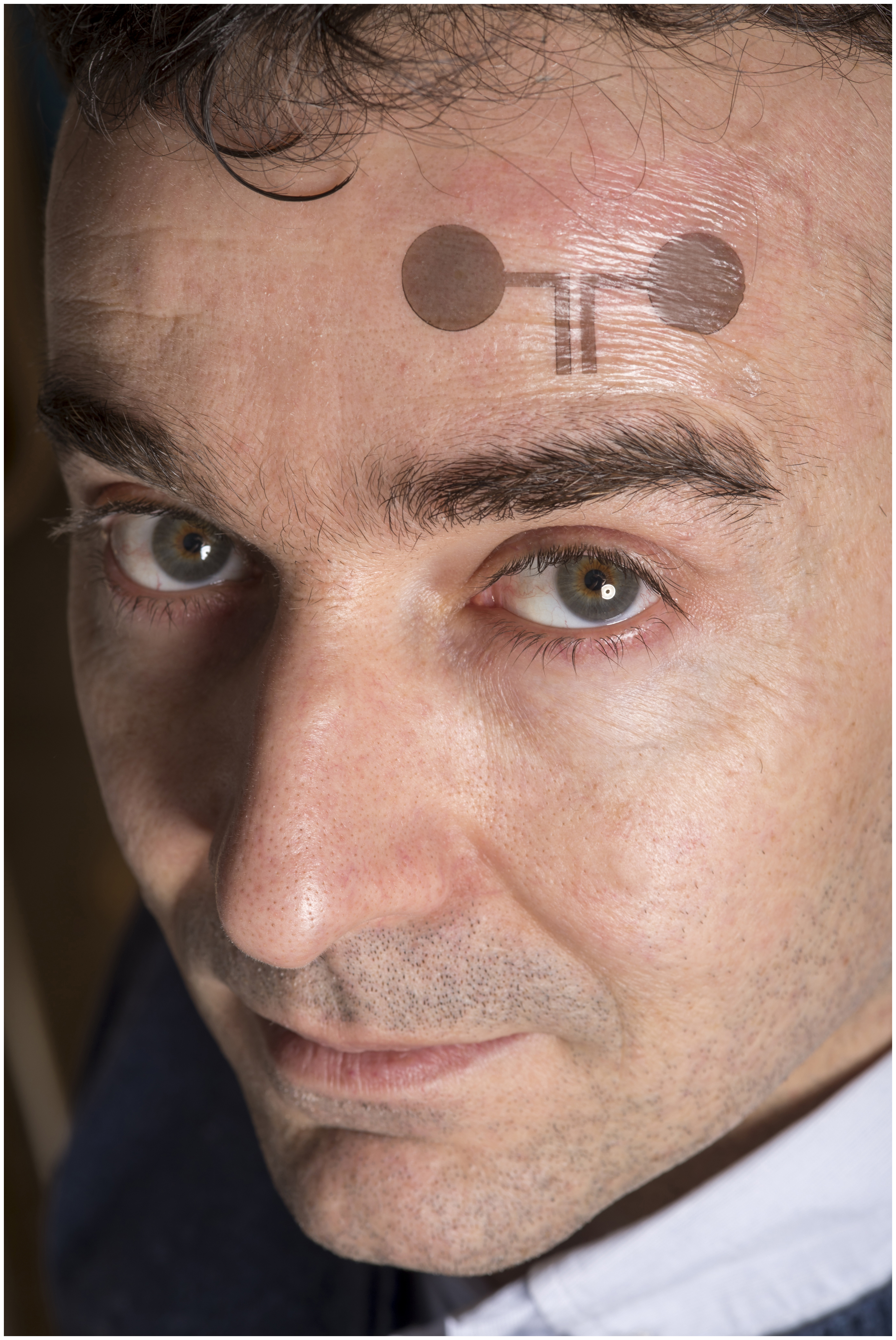
In the presented method, conducting polymers are printed on commercial temporary tattoo paper, thus producing single or multiple electrode arrangements. The external connections necessary for transmitting the signals are integrated directly in the tattoo. The tattoo electrodes are then applied to the skin like temporary transfer pictures and can hardly be felt by the wearer. Due to their extreme thinness of under one micrometre, the electrodes can be adapted perfectly to the uneven human skin, and can even be applied to parts of the body where traditional electrodes are not suitable, for instance the face. Francesco Greco, materials scientist at the Institute of Solid State Physics of TU Graz explains: “With this method we have managed to take a big step forward in further developing epidermal electronics. We are on a direct road to making an extremely economical and simple as well as versatile applicable system which has enormous market potential.” There is already concrete interest from international biomedical companies in the shared development of marketable products, Greco reports.Personalising epidermal electronics
Francesco Greco from TU Graz’s Institute of Solid State Physics is working together on this research topic with the team of Paolo Cavallari, professor of human physiology at Università degli Studi in Milan, and Professor Christian Cipriani, head of the Biorobotics Institute of Scuola Superiore Sant’ Anna in Pisa, and also with his former research group at Instituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT) Pontedera.
Kontakt
Dr.
TU Graz | Institute of Solid State Physics
Petersgasse 16/I, 8010 Graz
Tel.: +43 316 873 8471
E-Mail: <link int-link-mail window for sending>francesco.greco@tugraz.at